
#Carbon 14 decay constant skin#
The fraction of the radiation transmitted through the dead skin layer is estimated to be 0.11.

These are relatively low energies the maximum distance traveled is estimated to be 22 cm in air and 0.27 mm in body tissue. The emitted beta particles have a maximum energy of about 156 keV, while their weighted mean energy is 49 keV. This resemblance is used in chemical and biological research, in a technique called carbon labeling: carbon-14 atoms can be used to replace nonradioactive carbon, in order to trace chemical and biochemical reactions involving carbon atoms from any given organic compound.Ĭarbon-14 goes through radioactive beta decay:īy emitting an electron and an electron antineutrino, one of the neutrons in the carbon-14 atom decays to a proton and the carbon-14 ( half-life of 5,730 ± 40 years ) decays into the stable (non-radioactive) isotope nitrogen-14.Īs usual with beta decay, almost all the decay energy is carried away by the beta particle and the neutrino. The different isotopes of carbon do not differ appreciably in their chemical properties. However, open-air nuclear testing between 19 contributed to this pool. The primary natural source of carbon-14 on Earth is cosmic ray action on nitrogen in the atmosphere, and it is therefore a cosmogenic nuclide. A gram of carbon containing 1 atom of carbon-14 per 10 12 atoms will emit ~0.2 beta particles per second. Carbon-14 has a maximum specific activity of 62.4 mCi/mmol (2.31 GBq/mmol), or 164.9 GBq/g. Carbon-12 and carbon-13 are both stable, while carbon-14 is unstable and has a half-life of 5700 ☓0 years. There are three naturally occurring isotopes of carbon on Earth: carbon-12 ( 12Ĭ), which makes up 99% of all carbon on Earth carbon-13 ( 13Ĭ), which makes up 1% and carbon-14 ( 14Ĭ), which occurs in trace amounts, making up about 1 or 1.5 atoms per 10 12 atoms of carbon in the atmosphere. Its existence had been suggested by Franz Kurie in 1934. Carbon-14 was discovered on February 27, 1940, by Martin Kamen and Sam Ruben at the University of California Radiation Laboratory in Berkeley, California. Its presence in organic materials is the basis of the radiocarbon dating method pioneered by Willard Libby and colleagues (1949) to date archaeological, geological and hydrogeological samples.

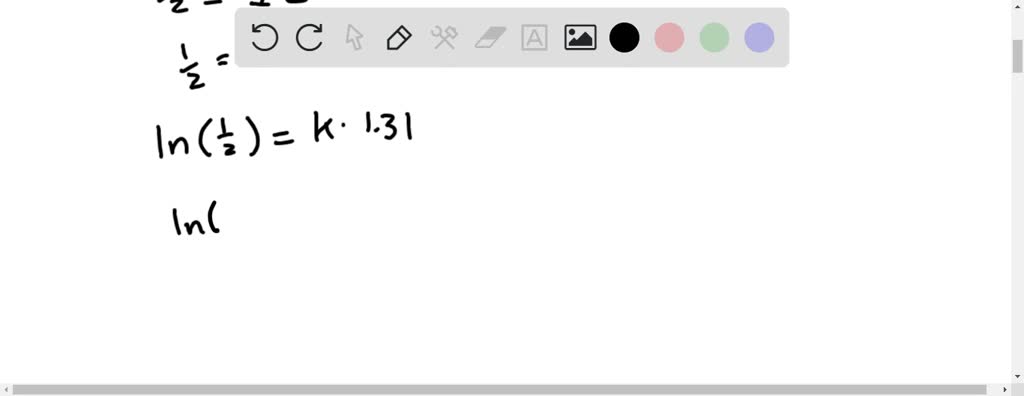
Carbon-14, 14Cġ part per trillion = 1 / 10 12 Ĭ or radiocarbon, is a radioactive isotope of carbon with an atomic nucleus containing 6 protons and 8 neutrons. For the dating technique, see Radiocarbon dating. For the scientific journal, see Radiocarbon (journal). The following equation gives the quantitative relationship between the original number of nuclei present at time zero (N_0\) and the number (\(N\)) at a later time \(t\)."Radiocarbon" redirects here.

It is also applicable to the decay of excited states in atoms and nuclei. The concept of half-life is applicable to other subatomic particles, as will be discussed in Particle Physics. Nuclides with the shortest half-lives are those for which the nuclear forces are least attractive, an indication of the extent to which the nuclear force can depend on the particular combination of neutrons and protons. \)y for the least unstable, or about 46 orders of magnitude.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
